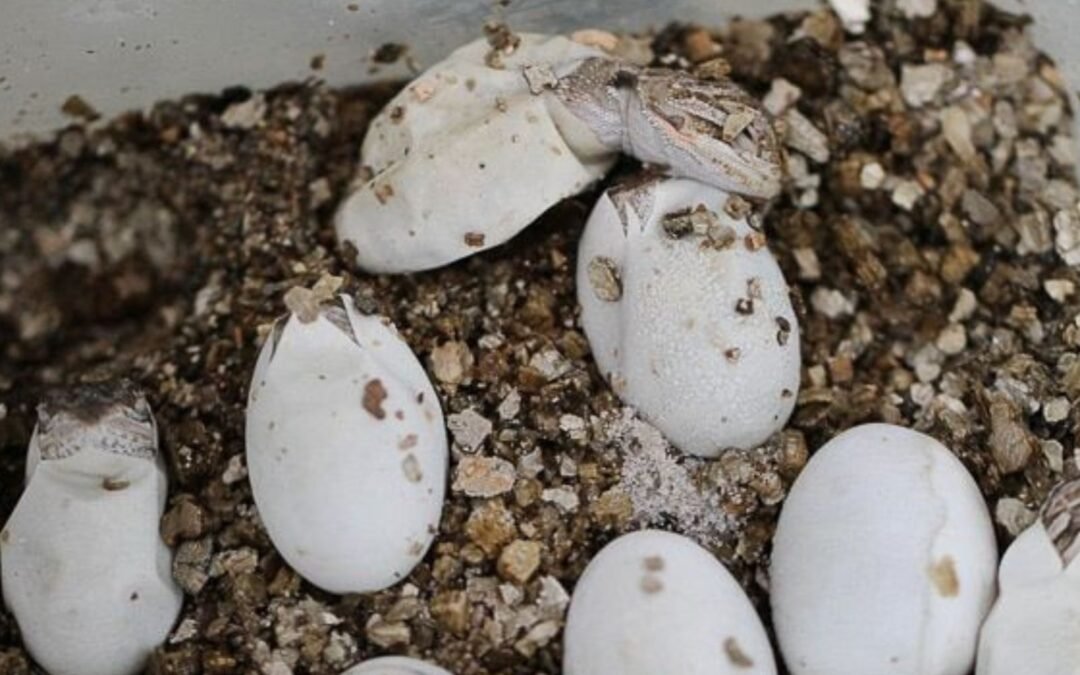
Bearded dragons are fascinating creatures, and when they lay eggs, it’s an exciting time for any reptile enthusiast. The arrival of bearded dragon eggs can spark a whirlwind of emotions—from anticipation to concern about their care. A successful hatch requires knowledge and attention to detail. Whether you’re a seasoned breeder or new to reptiles, understanding how to nurture these precious eggs is crucial.
In this guide, we’ll dive into everything you need to know about caring for bearded dragon eggs. We’ve covered you, from recognizing nesting behavior to ensuring proper incubation conditions! Embrace this journey with your scaly friend as we explore tips that will pave the way for healthy hatchlings and a rewarding experience. Let’s get started!
What to Do If Your Bearded Dragon Lays Eggs
When your bearded dragon lays eggs, the first step is to ensure her environment is safe and secure. Remove any potential stressors that could disrupt her or harm the eggs. Keep her habitat clean and provide fresh water to help maintain hydration.
Next, observe her behavior closely. A female may exhibit nesting behaviors like digging or becoming more reclusive when she lays eggs. Giving her space while ensuring she can access food and water is essential.
Consider creating one if a suitable nesting site still needs to be established. A lay box filled with moist substrate can encourage natural digging behavior and provide a comfortable spot for egg-laying, helping prevent accidental damage to the eggs.
After laying, gently examine the area where she laid them without disturbing their placement. Document the number of eggs laid to track their progress later during the incubation and care stages.
Bearded Dragon Nesting Behavior
Bearded dragons exhibit unique nesting behaviors that reflect their instincts. When a female is ready to lay eggs, she often seeks out a suitable location, which can be a soft substrate like sand or soil where she feels secure.
During this period, you may notice her digging and creating a small depression. It’s common for females to act restless or agitated as they prepare for egg-laying. They may also spend more time basking, signaling their hormonal changes.
Once she finds the right spot, she’ll begin laying her eggs precisely and carefully. The entire process can take several hours as she meticulously places each egg into the nest before covering it up.
After laying her eggs, she might display signs of exhaustion but eventually return to normal activity levels. Understanding these behaviors helps create an environment that supports your bearded dragon’s needs and successful breeding outcomes.
Problems With Bearded Dragons Laying Egg
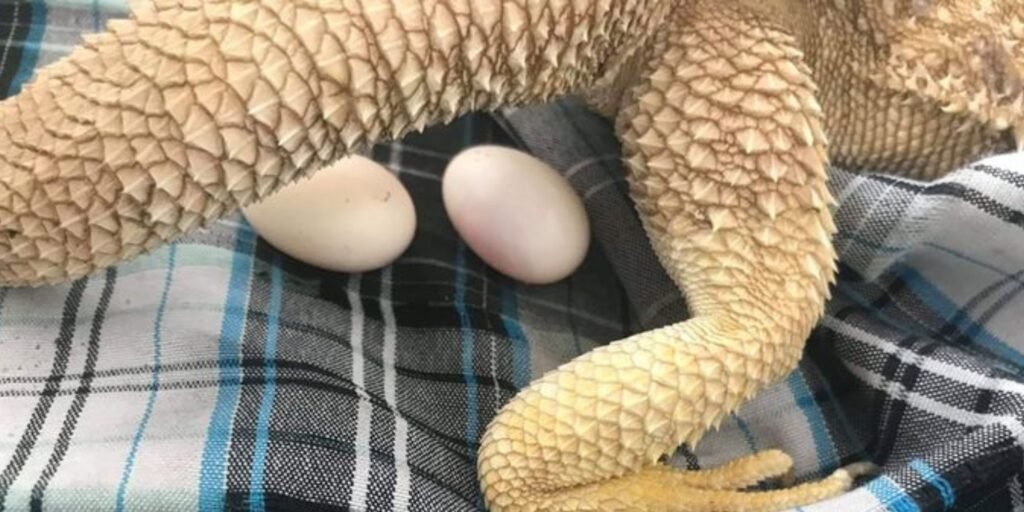
Bearded dragons often face challenges when laying eggs, leading to health issues for the mother and her offspring. One common problem is egg binding, where a female cannot pass her eggs due to various reasons such as dehydration or lack of proper nesting space. This condition is serious and requires immediate veterinary attention.
Another issue that may arise is stress caused by an inadequate environment during the breeding process. Factors like temperature fluctuations, improper humidity levels, or insufficient hiding spots can hinder a dragon’s ability to lay eggs comfortably. Stress not only affects the laying process but can also impact your pet’s overall health.
Bearded dragons may sometimes lay infertile eggs if not mated with a male. While these eggs won’t hatch, their presence can still create unnecessary worry for owners who might expect something different.
Monitoring your bearded dragon closely during this time is essential. Regular check-ups with a vet ensure any potential problems are caught early before they escalate into more serious concerns.
Bearded Dragon Egg Incubation and Care
Incubating bearded dragon egg is a critical step towards hatching healthy hatchlings. Once you have collected the eggs, ensure they are placed in an appropriate incubator. The ideal temperature for incubation ranges from 80 to 85 degrees Fahrenheit. Maintaining this temperature consistently is vital for the development of the embryos.
Humidity levels should also be monitored closely, aiming for around 60-70%. You can achieve this by using damp vermiculite or perlite as a substrate in your egg container. This moisture helps prevent the eggs from drying out, allowing enough airflow to support growth.
Turn the eggs gently every few days to mimic natural conditions; however, avoid excessive handling as it can cause stress or harm developing embryos. Depending on temperature and individual genetics, eggs typically hatch in about 55-75 days.
As you await hatching day, maintain a calm environment and resist unnecessary disturbances. Patience is key during this period; each moment counts toward welcoming new life into your home.
Where Should Bearded Dragons Lay Egg?
Choosing the right location for your bearded dragon to lay her eggs is crucial for her safety and health. Ideally, a dark, secluded area mimicking a natural burrow will provide comfort and security, which can help reduce stress during the laying process.
A suitable nesting box can be created using a container filled with substrate like coconut coir or moist sand. Ensure it’s deep enough—around 8-12 inches—for her instinctual digging behavior. Bearded dragons prefer warmer spots; maintaining an appropriate temperature in this area encourages egg-laying.
Monitor her closely leading up to the laying period. You may notice signs of restlessness or increased digging activity as she prepares to lay her eggs. It’s essential not to disturb her during this time; interference could disrupt the process.
Keep humidity levels in check, too! A slightly humid environment helps keep the substrate workable while preventing dehydration, vital for the mother and eggs during this delicate phase.
How Many Egg Do Bearded Dragons Lay?
Bearded dragons are fascinating creatures, especially when it comes to reproduction. A healthy female bearded dragon can lay a surprising number of egg. Typically, they will produce 15 to 30 eggs in one clutch. However, some females have been known to lay as many as 40 egg
The quantity can depend on several factors, including the dragon’s age and health, diet, and environmental conditions. Younger dragons or those experiencing their first breeding season might lay fewer eggs than more mature females.
Owners must monitor their pets’ behavior during this time; laying eggs is physically taxing. Proper nutrition and hydration help support them through this process.
After laying, these mothers often need extra care for recovery. Remember that egg-laying is a natural part of their life cycle; understanding how many eggs your bearded dragon lays allows you to prepare better for what lies ahead!
How to Tell If Bearded Dragon Eggs Are Fertile
Determining the fertility of bearded dragon egg can be crucial for an anxious reptile owner. One of the first signs to look out for is their appearance. Fertile eggs are typically smooth and firm and have a slightly glossy surface. If you notice any irregularities or rough textures, it could indicate infertility.
Another method of checking fertility is candling. This technique involves shining a bright light through the egg in a dark room. Fertile eggs often display visible veins and a developing embryo, while infertile ones may appear clear or contain only yolk without further development.
Timing also plays a role in assessing fertility. Check your incubating schedule; fertile eggs usually take around 60 days to hatch under optimal conditions. If they don’t show signs of hatching after that period, they may not be viable from the start.
Consider the behavior of your female before laying her eggs. Mated females are more likely to produce fertile clutches than those who have not mated recently.
Caring for Fertile Eggs
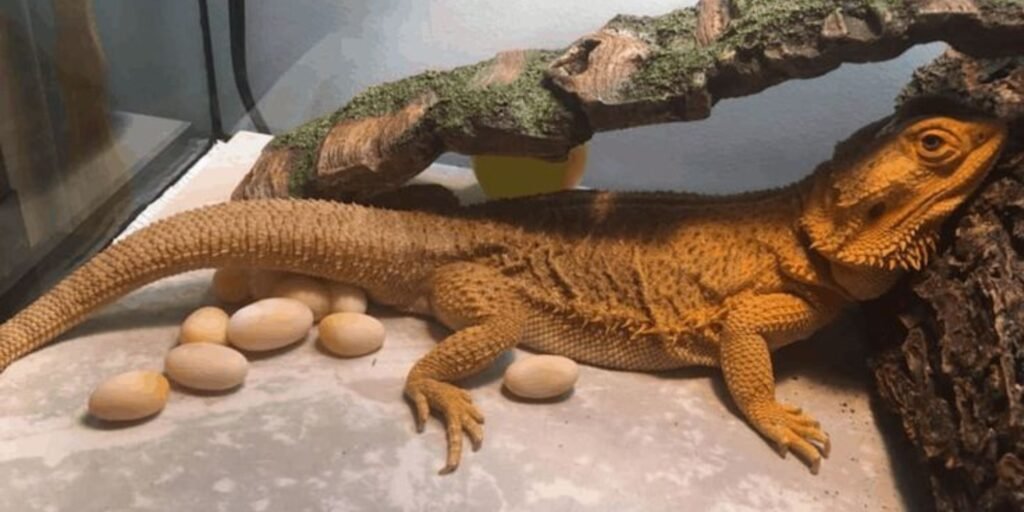

Caring for bearded dragon egg requires attention and diligence. Once you have confirmed that the eggs are fertile, your focus shifts to creating a suitable environment for them to grow.
Start by maintaining consistent humidity levels between 60-70%. Use a hygrometer to monitor this closely, as too much or too little moisture can lead to problems. The substrate should be damp but not soaked; consider using vermiculite or perlite, as they provide excellent moisture retention without overwhelming the eggs.
Temperature is another crucial factor—aim for around 80-85°F (27-29°C) in your incubation area. For optimal results, you may utilize an incubator with adjustable settings. Be mindful of frequent temperature fluctuations, which can inhibit proper development.
Regular checks on your eggs are essential. Look out for any signs of mold or decay and remove affected eggs immediately if needed. Patience is key; depending on conditions, most clutches will hatch within 55-75 days,

